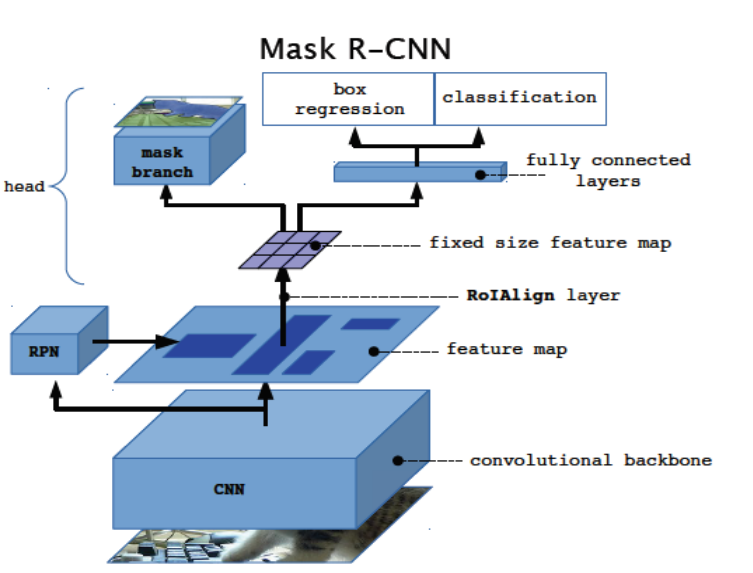
The Mask R-CNN (Regional Convolutional Neural Network) can be used in instance segmentation, and has been quite sucessful when compared with other architectures for the same task. In this project we look at its performance on two well known datasets, cityscapes and CSAIL Places, and try to see the impact of modifying hyperparameters and using different network architectures in the backbone.
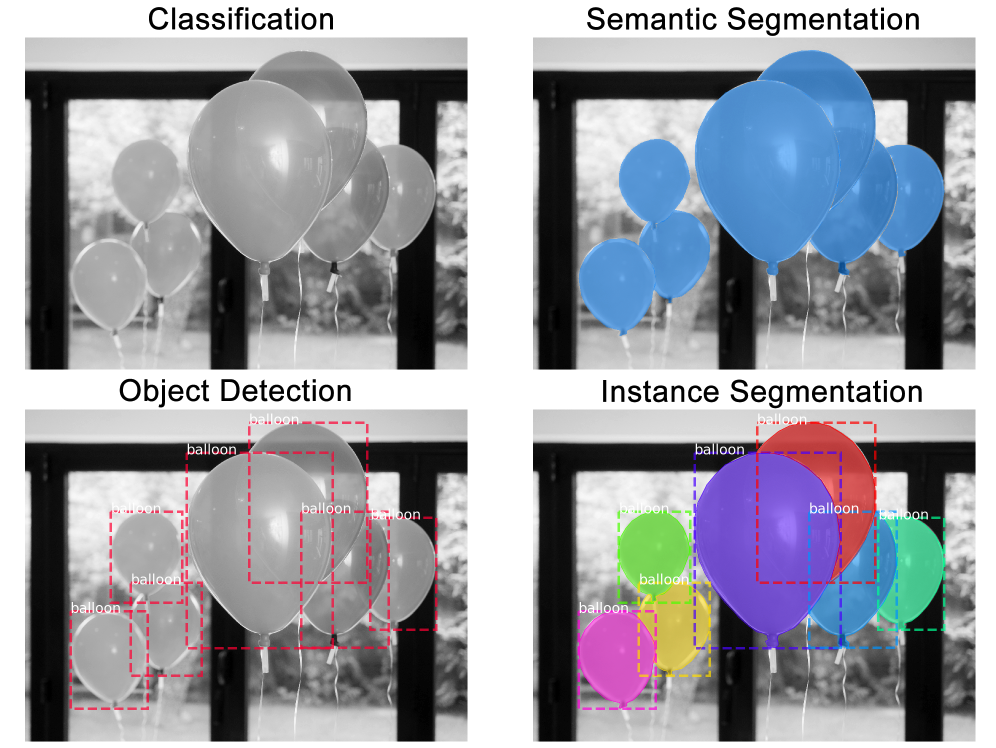
- Summary of the Problem Instance Segmentation is the combination of three other tasks making it very difficult. Those three tasks are Image Classification, Object Detection, and Semantic Segmentation. See Figure 1 for an overview of the task.
Instance Segmentation
Image Classification, being the most studied of the three, is a task where you are given an image and the goal is to classify it. Examples of such studies are those done on the MNIST dataset [1]. In MNIST, the task is to classify handwritten digits given only an image of the digit. Some of the most successful approaches involve CNN architectures, like VGG, GoogleLeNet, ResNet, and many others. Object Detection has the same domain, but the goal is to find all instances of an object and find the smallest bounding box around the object. One way to structure this as a machine learning task is to formulate it as a Regression problem, where the bounding box is defined by a set of coordinates. This is done in our Mask R-CNN implementation and its immediate predecessor, Faster R-CNN [2]. The goal of Semantic Segmentation is to classify each pixel, effectively segmenting an image into its semantic components. This was a difficult task because there was no obvious way to generate predictions for each pixel, without feeding the whole image multiple times through a traditional CNN classification network, and this would make the problem intractable. One well known solution to this is to use a Fully Convolutional Network (FCN), which would have an Encoder/Decoder structure by first using Convolution Layers and Pooling
Cityscapes Cityscapes has data from street scenes, so an application of a network trained on this dataset is autonomous vehicles. The dataset has approximately 5,000 examples and 30 classes with fine grain annotations. We used about 3,500 for training and 500 for validation.
CSAIL Places This dataset is more general and has a wide variety of scenes. It has approximately 20K examples (2K validation), with annotations, and 100 classes. The CSAIL places dataset will give us an opportunity to compare our results with work published that tested with more popular datasets like MSCOCO [4].
Mask R-CNN Architecture